Presentation of Case
A 27-year-old man was admitted to the hospital because of a syncopal episode.
This man had been well until yesterday morning, when he suddenly lost consciousness while playing basketball.His teammate reported that“he fell backward to the ground,striking the back of his head.He regained consciousness and recovered fully in less than one minute without any resuscitation.”The patient claimed that he experienced neither palpitations nor any prodromal symptom.However,about three years earlier before this presentation,he had a brief syncopal episode.EKG at that time showed no specific abnormality.He denied taking any medications,but had a family history of sudden cardiac death in his uncle.His teammate brought him to the emergency department at this hospital.
On examination,the patient was alert and oriented.The temperature was 36.8°C,the pulse 80 beats per minute, the blood pressure 115/75 mmHg, and the oxygen saturation 100% while he was breathing ambient air.There was no sign of head or facial trauma,and examinations of the cranial nerves were normal.No cardiac murmur was detected on auscultation,and the breath sounds were clear.The remainder of the general physical and neurologic examinations was normal.
A chest radiograph showed no evidence of edema, pleural effusion,or tapering of artery.His resting EKG revealed normal sinus rhythm without prolongation of the QT interval.Routine laboratory tests and urinalysis were performed.
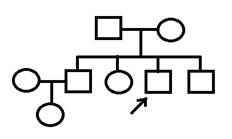
< Pedigree >
<Laboratory data>
CBC/DC: (Time: January 15, 2013)
WBC /μL |
7400 |
Blast % |
0 |
Mono % |
3 |
RBC M/μL |
4.2 |
Promyl % |
0 |
Lym % |
31 |
Hb g/dL |
14.0 |
Myelo % |
0 |
Aty. Lym % |
0 |
Hct % |
42.0 |
Meta % |
0 |
Plasma cell % |
0 |
MCV fl |
85.7 |
Band % |
0 |
|
|
PLT. /μL |
320000 |
Seg % |
65.5 |
|
|
|
|
Eos % |
3.0 |
|
|
|
|
Baso % |
1.5 |
|
|
Biochemistry: (Time: January 15, 2013)
BUN |
mg/dL |
9.0 |
Na |
mmol/L |
140 |
Sugar AC mg/dL |
95 |
Cre |
mg/dL |
0.5 |
K |
mmol/L |
4.8 |
|
|
T-Bil |
mg/dL |
0.73 |
Ca |
mmol/L |
2.35 |
|
|
ALT |
U/L |
30 |
Mg |
mmol/L |
0.90 |
|
|
Urinalysis: (Time: January 15, 2013)
SpGr |
1.015 |
RBC |
HPF |
0-2 |
pH |
5.8 |
WBC |
HPF |
0-2 |
Protein |
- |
Epi |
HPF |
0-2 |
Glucose |
- |
Cast |
|
- |
Ketones |
- |
Nitrite |
|
- |
OB |
- |
Crystal |
|
- |
Course and Treatment
Transthoracic echocardiogram showed normal ejection fraction of the left ventricle (M-mode: 75%) without any structural abnormalities or elevated pulmonary pressure.24-hour Holter monitoring did not reveal any arrhythmias.Exercise EKG showed ventricular tachycardia. Genetic analysis revealed homozygous missense mutation in CASQ2. Propranolol 40 mg BID was given, and he remained asymptomatic.His parents and siblings were evaluated with EKG,Holter monitoring and exercise stress test, and all the screening tests were normal,but his father and mother have the heterozygous mutation in CASQ2.
< Exercise EKG > (Time: January 16, 2013)
Discussion
Syncope的真正定義為失去意識後能快速且自然恢復到原本的狀態,並無任何新的局部性神經功能缺損。當一位病患因為syncope到急診就診,當前要務就是區分syncope的原因是否攸關生死,例如cardiac syncope,blood loss,pulmonary embolism,和subarachnoid hemorrhage,其他如seizure,stroke,和head injury也是需要先釐清的。(請見Figure 1)
Figure 1
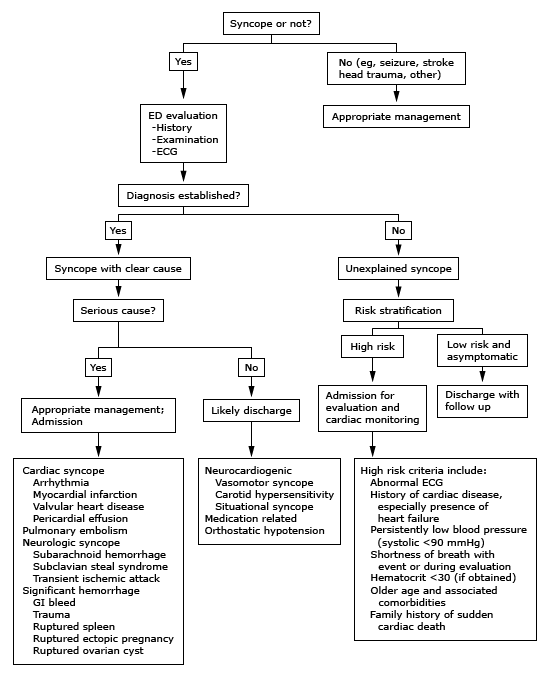
危及生命的情況: (請見Table 1)
- Cardiac syncope: 最常見危及生命的syncope原因就是cardiac syncope,包含了心律不整、ischemia(例如,acute coronary syndrome、myocardial infarction)、結構性的異常(例如,aortic stenosis)、cardiac tamponade,和心律調節器故障。
- Blood loss: trauma、gastrointestinal bleeding、ruptured aneurysm、rupture spleen、ruptured ectopic pregnancy。
- Pulmonary embolism
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Table 1
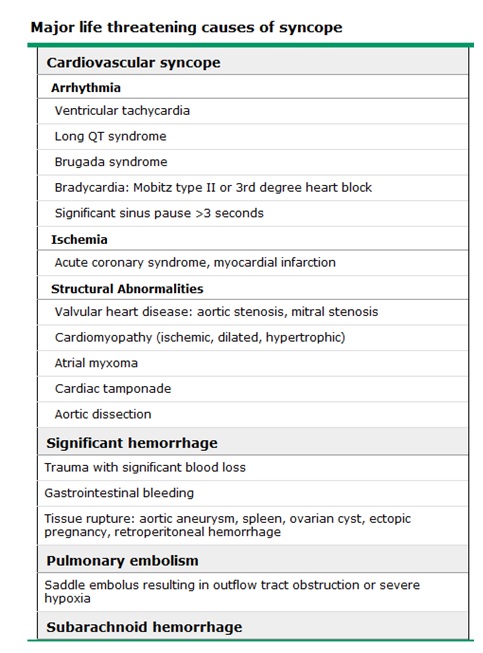
常發生的情況: (請見Table 2)
- Neurocardiogenic syncope (vasovagal syncope): 最常造成syncope的原因,占了25~65%。大部分的患者歷經了頭暈、噁心、嘔吐、冒汗等prodrome,例如micturition或defecation syncope、cough-mediated syncope、situational syncope(例如,抽血)。
- Carotid sinus hypersensitivity: 常見的原因有刮鬍子、領口太緊、轉頭時等外力所造成的反射反應。
- Orthostasis: 占syncope約5~24%,定義為改變姿勢時血壓掉了20 mmHg以上,或是反射性的心搏過速(每分鐘多跳20下以上)。
- Medications: 占syncope約5~15%,常見的有CCB、alpha & beta blockers、antiarrhythmics、diuretics、影響QT interval的藥物如antipsychotics等。
Table 2
其他的情況:
- Neurologic syncope: Syncope的真正定義為失去意識後能快速且自然恢復到原本的狀態,並無任何新的局部性神經功能缺損,所以真正屬於神經系統導致性的原因比較少。如 subarachnoid hemorrhage、transient ischemic attack、subclavian steal syndrome等。有時syncope或seizure容易混淆,相較於seizure,syncope的抽搐時間較簡短且沒有發作後期(postictal phase)。
- Psychiatric syncope:焦慮和恐慌症可能造成situational syncope,這類病患相對年輕,沒有心臟疾病,且多次發作
- Drug induced loss of consciousness:藥物或酒精濫用也可能導致syncope,但這類患者會有其他中毒表現
- Metabolic:如低血糖或缺氧
- Rare causes:如atrial myxoma、Takayasu's arteritis、carcinoid
這位病患自述在syncope發生時正在打籃球,並沒有經歷頭暈、視力模糊、噁心、嘔吐、冒汗、心悸等prodrome,隊友也說他突然失去意識倒下去,但不到一分鐘自然醒過來,這之間除了搖動他外,並沒有給予CPR或是任何急救,而且患者並沒有發生抽搐、咬舌、或出現postictal phase,醒來後也沒有頭出血、噁心、嘔吐、胸痛、心悸、或尿失禁等症狀。三年前同樣也是在打籃球時發作,當初在急診做的EKG並沒有任何異常。患者本身過去沒有任何的疾病,也無自行服用藥物、酒精、或毒品,家族裡有人突然猝死疾病。根據初步的病史詢問,cardiac syncope無法完全排除,可能性最大。
Physical examination沒看到外觀受傷或是聽到heart murmurs, neurologic examination沒有發現focal neurologic deficits,抽血報告沒有血糖異常或電解質不平衡,這些客觀的negative findings顯示這不太像是metabolism或是神經性的因素造成的syncope。Resting EKG顯示沒有QT interval prolongation,但無法完全排除long QT syndrome的可能性,因為有1/3 long QT syndrome 病人靜態心電圖QTc是正常的。此病人心臟超音波和24-hour Holter monitoring的結果是正常的,並無結構性的心臟病如AS等或是有紀錄到心律不整。但是,運動心電圖卻出現bidirectional VT,再加上genetic testing也證實在CASQ2有missense mutation,所以這位患者的最終診斷為catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia。除了病患本身的治療外,一等親的家人跟兄弟姊妹也建議做genetic screening,以區別及找出高危險的家屬。
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia的介紹
Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) 是一種好發在小孩子的疾病,平均發病年齡為7~9歲,但在成年人也有可能發病。大約有30%的患者曾歷經過至少一次心跳停止,死亡率高,必需早期診斷早期治療。特徵是在運動中或是突然情緒激動導致昏厥,患者本身沒有結構性的心臟病。目前已知RYR2和CASQ2的基因突變是造成CPVT的主要原因;其中,RYR2為自體顯性遺傳,CASQ2為自體隱性遺傳。CPVT的症狀包括了心律不整、頭暈、昏厥等,會造成這些事件的原因是VT (bidirectional or polymorphic)。當心律不整自行終止後,病患會自行恢復。倘若心律不整沒有停住,VT可能會發展成ventricular fibrillation且造成sudden death。
Resting EKG通常是正常的,gold standard檢查為exercise stress test(運動心電圖),因為急性的腎上腺素活化(例如運動、突然情緒激動)可以引起典型的VT。雙向性心跳過速(bidirectional tachycardia)的定義為每下反向的ventricular arrhythmia,但這種VT只佔CPVT病人的1/3,大部分患者為多型性心室頻脈(polymorphic VT)。運動中心律不整通常出現在心跳閾值為每分鐘100~120下左右,且負荷量愈大愈會讓心律不整的狀況惡化。CPVT診斷流程請參考Figure 2。
Figure 2
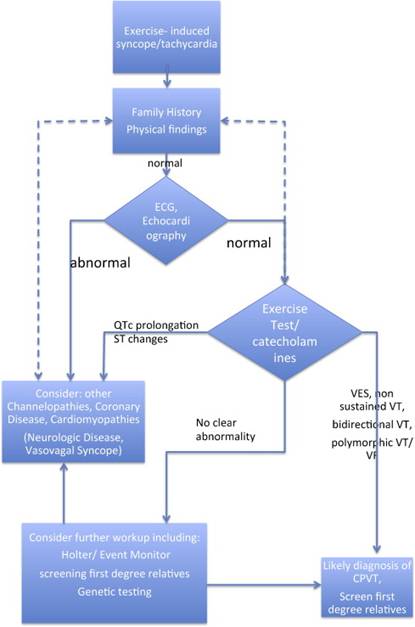
Beta-blockers為CPVT最主要的治療方式,例如nadolol (1-2.5 mg/kg/day)或propranolol (2-4 mg/kg /day)。如果病患已在服用beta-blocker卻還是反覆發生心跳停止,或是病人無法服用beta-blocker時,植入型心臟去顫器(ICD)也許是必要的。所有有症狀的病患都應該服用beta-blockers;假設患者有RYR2的基因突變,就算沒有經歷過昏厥或是運動中產生VT,或許也該服用beta-blockers。病患平常應避免競技體育等劇烈運動,且每六到十二個月應該回心臟科醫師門診追蹤治療效果。
由於治療和監測可以減少發病率和死亡率,當已知家庭特異性突變(family-specific mutation)時,強烈建議患者的第一等親接受分子基因檢測。如果不知家庭特異性突變,強烈建議患者所有的第一等親接受resting EKG、Holter monitoring、exercise stress test的評估。
總而言之,根據此病人的臨床表現(syncope while playing basketball)、resting EKG(沒有QT interval prolongation)、exercise stress test(VT)、實驗室檢查(genetic test: homozygous missense mutation in CASQ2),得知此病人的診斷為catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia,所以除了藥物治療,也需對其family members做genetic testing,開始追蹤其治療效果。
References:
- Nederend I,van der Werf C, Wilde AAM. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia in 2012.Cardiogenetics 2011;1(s1):e4.
- Pflaumer A,Davis AM. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia.Heart,Lung and Circulation 2012;21:96-100.
- Moya A,Sutton R,Ammirati F etc.Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of syncope (version 2009).European Heart Journal (2009) 30, 2631-2671.
- McDermott D, Quinn J.Approach to the adult patient with syncope in the emergency departmentUpToDate:http://www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-adult-patient-with-syncope-in-the-emergency-department?detectedLanguage=en&source=search_result&search=syncope&selectedTitle=2%7E150&provider=noProvider#
- Napolitano C, Priori S,Bloise R. Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia.GeneReviews.Pagon RA, Adam MP,Bird TD,et al.,editors.GeneReviewsTM[Internet].Seattle (WA):University of Washington,Seattle; 1993-2013.Available from:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/
|